Simple Tips to Help Diagnose and Prevent Windows Server Crashes
In an enterprise setting, server failures are never an issue to be taken lightly. Since servers are the backbone of most modern operations, being able to pinpoint the cause of errors rapidly is an essential skill for any Windows server administrator. Fortunately by following a few simple steps you can easily pinpoint the cause of most Windows Server errors.
Best Practice Analysis Automation
In Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2, Microsoft has included a tool known as the Best Practices Analyzer (BPA). BPA is an automated scanner which when run will check your server to ensure that it is configured for optimal performance, reliability and maximum security. While this tool is not a substitute for keeping atop of Windows Server trends, BPA helps to ensure that the most commonly exploited violations are blocked on your servers.
The Windows Server 2012 and Windows Server 2012 R2 BPA documentation can be found here while the Windows Server 2008 R2 documentation is here.
Proactive Actions to Simplify Troubleshooting
Enable Kernel Crash Dumps
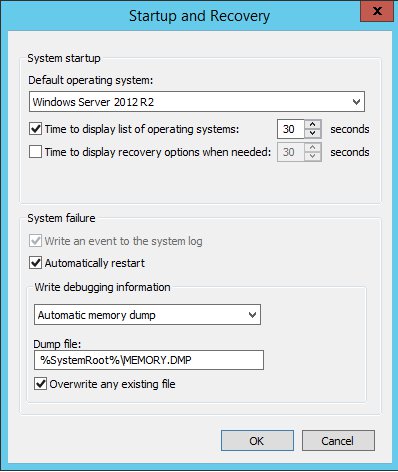
One of the most important debugging tools within Windows is the kernel crash dump file. This file typically contains all the information necessary to pinpoint the cause of a server issue. Unfortunately this feature isn’t configured by default, making it crucial that you enable this feature before experiencing issues.
To enable this feature, follow the steps below:
- Go into:~ Control Panel > System and Security > System.
- Click Advanced system settings.
- Under Startup and Recovery, click Settings
- In the box that pops up, under Write Debugging Information you can specify the location for the crash dump file
- Additionally you can have crashes added to the Windows Event Log, and you can also trigger a restart automatically upon a crash
Enable Keyboard Crash Dump Commands
After configuring the Windows crash dump settings, you will need to setup Windows to enable your keyboard to cause a system crash.
With PS/2 keyboards, you must take the following steps:
- In the registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\i8042prt\Parameters, create a value named CrashOnCtrlScroll
- Set it equal to a REG_DWORD value of 0x01.
- Restart your system
With USB keyboards, you must take the following steps:
- In the registry key HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\kbdhid\Parameters, create a value named CrashOnCtrlScroll
- Set it equal to a REG_DWORD value of 0x01
- Restart your system
Windows Debugging Tools
To help with common issues that might come up as a server administrator Microsoft has released multiple debugging tools to make the job easier.
Sysinternals Suite
The Sysinternals suite is like a Swiss Army knife for your troubleshooting efforts. This collection of seventy tools maintained by Microsoft ensures that you can easily pinpoint the source of virtually any error and take action accordingly. While this suite is best installed on a thumb drive to be used when errors occur, you can also load this suite on your servers early on as a proactive measure.
While there are many tools within the suite, there are a couple which you should keep on mind;
- Disckmon – this tool monitors, logs and displays all hard disk activity on a Windows system. By using this tool, you can better pinpoint errors which might be caused by pending hard disk failures.
- Procdump – this tool allows you to monitor applications for CPU spikes and generating crash dumps during a spike. Additionally the tool can serve as a general dump utility which can be included in other scripts. By using this tool, you can greatly expedite the process of diagnosing troublesome applications and figuring out where to start debugging efforts.
- TCPView – this tool allows you to view detailed listings of all TCP and UDP endpoints on your system. By using TCPView, you can pinpoint server issues to specific ports, allowing you to more in-depth action accordingly.
Windows Memory Diagnostics
Since RAM is one of the most used components of any server, many system failures often are due to memory-related matters. While typical memory issues involve applications using too much resources, or a process running out of control, failing hardware also can be responsible for system crashes. Fortunately you can easily diagnose potential memory trouble spots by using the Windows Memory Diagnostics tool built into most modern Windows Server editions.
To use this tool, simply open the command prompt and use the following command C:\mdsched
From there, you should follow the prompts to complete the diagnostic process.
The Importance of Backups
Even with the best tools and skills, occasionally a professional will encounter an issue which is beyond repair. When situations such as these occur, having a solid backup system always pays off. Although there are many backup tools on the market, Windows has a backup tool built in which can be used to protect yourself from even the worst disasters.
For details on implementing Windows Backup in windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2012, Microsoft has documentation here.
Clustering as a way to Mitigate Risks
Server clustering is the process of having a group of independent servers working together as a single system to deliver more reliability to your users. Such arrangements are designed to protect against the following types of failure:
- Applications and service failures which can affect software and essential services
- System and hardware failures which can affect low level server components
- Site failures in multisite organizations ~which can be caused by natural disasters and other significant situations
By using clustering, you can ensure that when disaster strikes, your systems can continue operating instantly by shifting responsibility from the failed systems to the functional ones.
For information on clustering in Windows Server 2008 R2, Microsoft has a guide here. Windows Server 2012 documentation can be found here.
Conclusion
Although there are many variables which impact the reliability of your Windows servers, by focusing on proactive actions to mitigate damage you can avoid the difficulties of troubleshooting server issues. Even with the best precautions however, failures still occur, which is why you should familiarize yourself in advance with the technologies Windows provides to make the debugging process much easier.