Monitor over 100 Azure resources with Site24x7's Azure monitoring tool for optimal Azure performance.
Deploying frontends on Azure
Microsoft Azure is a global cloud platform for hosting and managing applications that employs well-defined interfaces and asynchronous messaging. Azure has redefined how contemporary intelligent frontend applications can be deployed, starting from monolithic architecture to microservices architecture containing smaller, decentralized containerized app services.
Intelligent web and mobile frontend can scale horizontally and is designed to anticipate and recover from failure. Static web apps, mobile frontends, and API apps can be deployed over frequent small updates with automated self-management and immutable infrastructure.
The applications can be hosted through a continuous integration and continuous delivery or deployment (CI/CD) pipeline from a Git-based version control system that maintains the development, test, pre-production, and production stages.
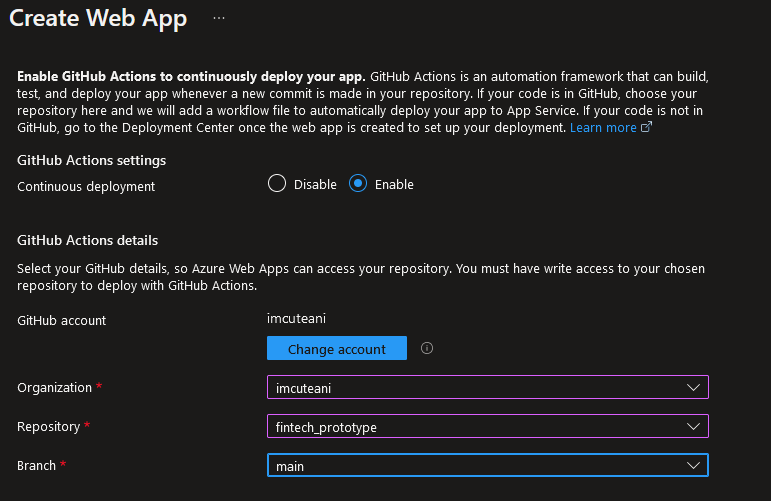 Fig 1: CI/CD pipeline deployment configuration of Azure App service
Fig 1: CI/CD pipeline deployment configuration of Azure App service
Application- and platform-level security is also integrated in the CI/CD pipeline by applying reliability and high availability.
Frontend application deployment with Azure App Service
Azure App Service is a fully managed service that offers built-in infrastructure maintenance, security integration, automated scaling, and increased availability and durability. Web applications, API apps, and mobile apps can be deployed through CI/CD devops pipeline.
The application deployment slots can be swapped from development to production and vice versa.
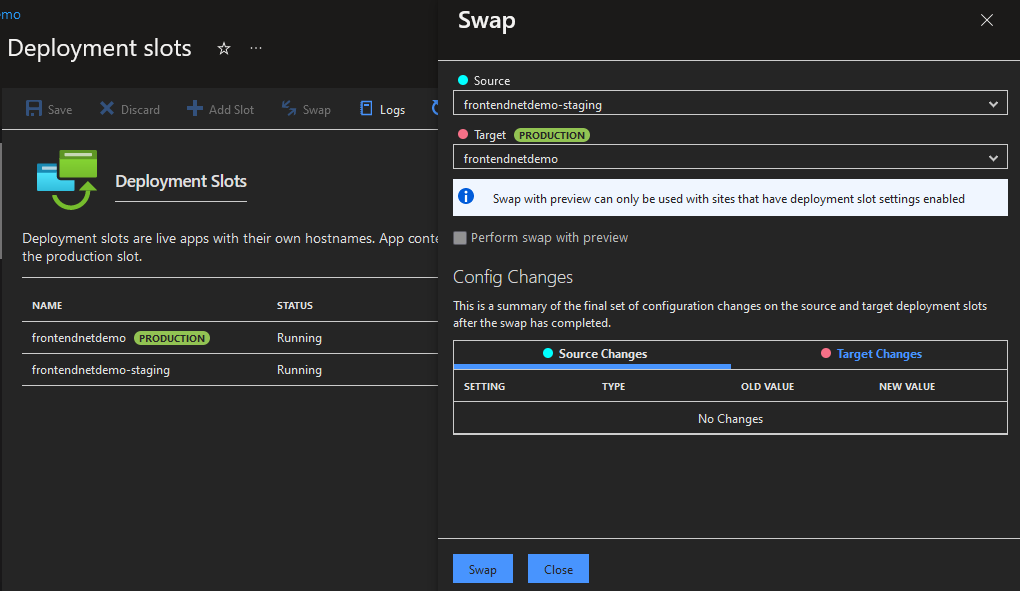 Fig 2: swap of deployment slots from development to production in Azure app service
Fig 2: swap of deployment slots from development to production in Azure app service
Frontend applications (web and mobile/API) can be deployed over code, Docker or Kubernetes containers, or as static web applications, including hosting support over a dedicated virtual network and secure private endpoint.
Deploying .NET/React web applications on Azure
Azure App Service supports various languages and frameworks, for example ASP.NET v4.8, ASP.NET v3.5, .NET6 or .NET7, Go, Java, Node.js, Python, and Ruby. It provides the flexibility to publish over various slots like Docker containers, code, or static web applications; it also offers scalability, runtime stack, security, and monitoring support, including a deployment facility on Windows or Linux.
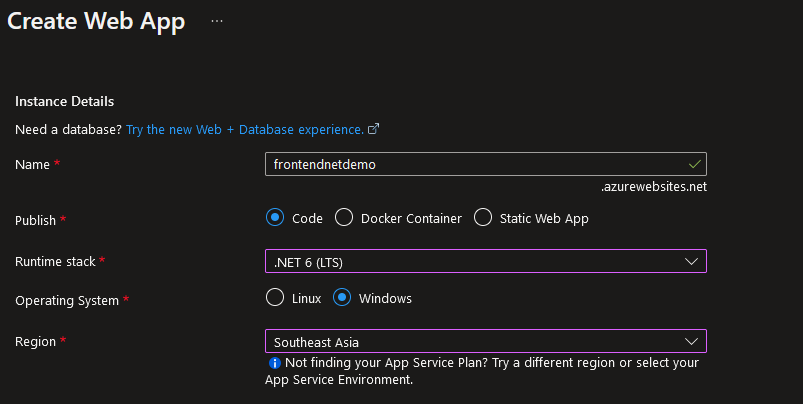 Fig. 3: Provisioning an Azure App service web app with publish stack
Fig. 3: Provisioning an Azure App service web app with publish stack
Frontend applications (i.e. web, mobile, and API apps) can be published over app service plans, including Windows and Linux platforms, based on app deployment region. Azure App Service offers support for different stock keeping units (SKU) and multiple tiers, including the Basic, Premium, and Isolated plans.
- The Basic tier supports 100 Azure compute units (ACU), 1.75 GB memory, and 1 vCPU core.
- The Premium V3 tier supports 195 ACU, 8/16/32 GB memory, and 2/4/8 vCPU cores.
- The Isolated V2 tier supports 195 ACU, 8/16/32 GB memory, and a maximum of 8 vCPU cores.
The Azure App Service plan provides all the benefits of zone redundancy in terms of high availability and replication. While zone redundancy is enabled, it replicates three app service instances on three availability zones of the deployment region.
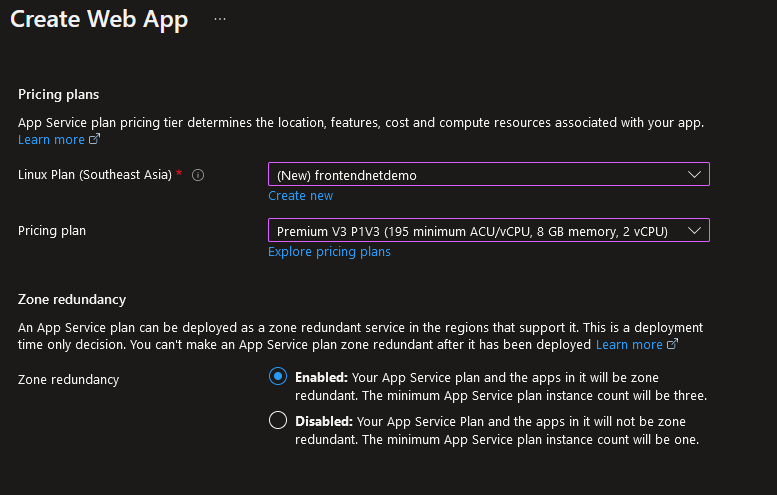 Fig. 4: Azure App Service plans and zone redundancy support
Fig. 4: Azure App Service plans and zone redundancy support
Azure App Service allows integration with GitHub actions for application deployment. This automation framework can assist with building, testing, and deploying applications from a source control repo like Github, GitLab, Bitbucket, or Azure DevOps Git. Frontend apps can be deployed through App Service provisioning on an isolated Azure virtual network. The outbound traffic can be segregated and filtered based on network security groups or through dedicated private IPs like Private Link.
VNet injection grants granular-level access to the Azure App Service environment only through the Azure VNet subnet CIDR or IP address ranges, including integration support with on-premise networks. It provides the benefits of network isolation and helps deployment over the app service instances on service endpoints or private networks. Deploying web or API apps over private endpoints is mandatory for the production environment since it connects end users through dedicated private IPs in a dedicated VNet, with private DNS zone support for both inbound and outbound traffic.
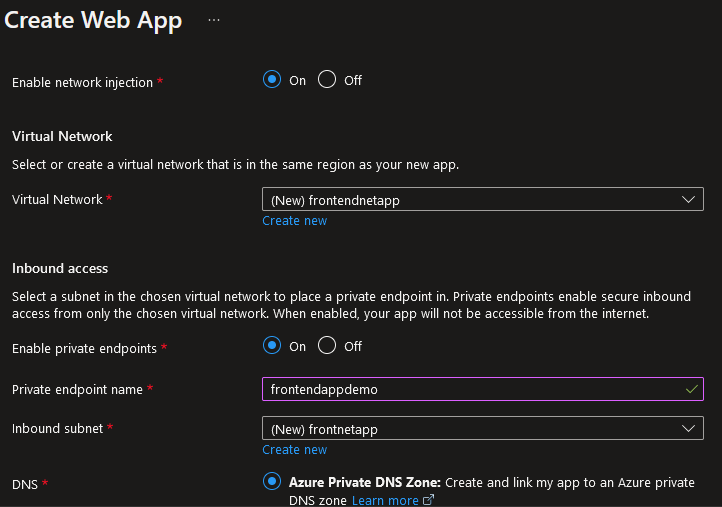 Fig. 5: Integrating VNet injection with Azure App Service
Fig. 5: Integrating VNet injection with Azure App Service
Azure Monitor is an application performance management (APM) feature on Azure App Service used to automatically monitor an application’s infrastructure and health, as well as infrastructure compute capacity metrics like CPU core usage, memory, disk I/O, and network I/O. It can detect performance anomalies and will share the activity logs, diagnostics logs, and traces to collect for troubleshooting.
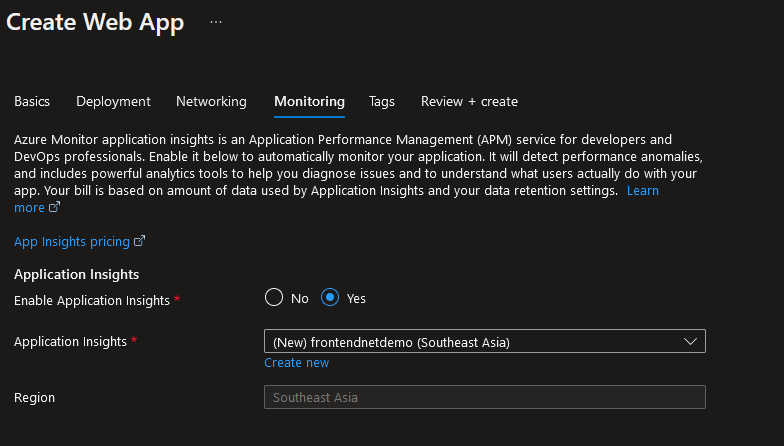 Fig. 6: Application Insights (APM) integration with Azure App Service
Fig. 6: Application Insights (APM) integration with Azure App Service
-
Azure App Service can integrate with various identity providers, such as Azure AD, Microsoft Graph API, Google, GitHub, Twitter, Apple, or OpenID Connect. To authenticate and authorize on Azure AD, an app registration ID is required.
When registering an application, the client secret and client ID are obtained as part of the service principal credential settings. The Microsoft identity platform authenticates users and provides security tokens. There is a dedicated token store that refreshes tokens for performance optimization.
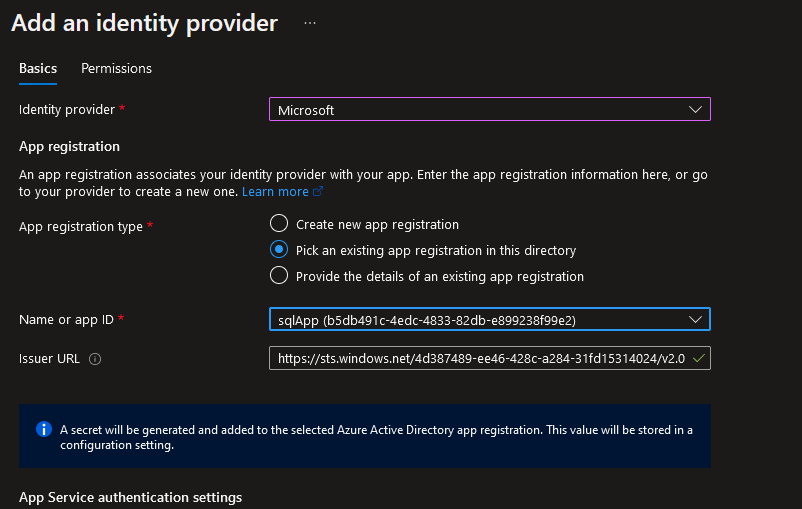 Fig. 7: Azure AD application registration with Azure App Service
Fig. 7: Azure AD application registration with Azure App Service
-
Azure App Service supports horizontal scaling (scale out) and vertical scaling (scale up) capabilities. App Service instances can be scaled up to higher compute capacity units based on DevTest or production tiers of various ACU/vCPU core and memory configurations—or they can be scaled down based on workload traffic requirements. Similarly, the number of application instances can be increased or decreased depending on the workload.
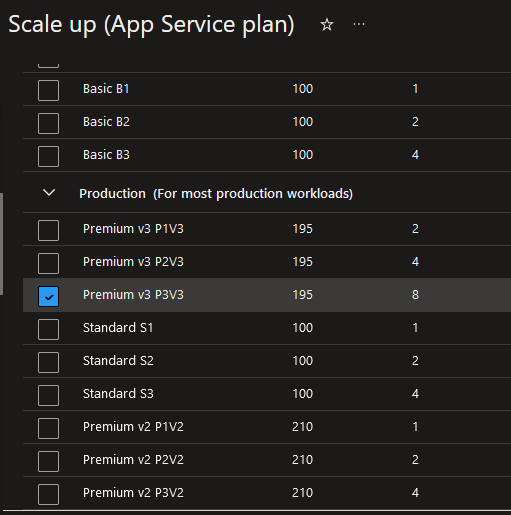 Fig. 8: Scale up configuration of Azure App Service plan
Fig. 8: Scale up configuration of Azure App Service plan
The Azure App Service platform can integrate self-signed, public-key certificate (CER), or CA-authorized certificates to manage security. The certificates can be hosted with the custom domain, which enables the custom domain registration facility and configures the CNAME record of the web hosting domain with A records for the IP address of the respective web app’s DNS settings.
-
App Service also provides deployment slots for hosting live applications with custom domains and their own host names. A deployment slot provides an additional hosting environment over the default production slot. Deployment slots can be swapped from staging to the production environment and back across all Azure App Service tiers.
Configuration settings such as connection strings, certificates, WebJobs, service endpoints, and Azure Content Delivery Network (Azure CDN) configurations are swapped for the deployment swap operation.
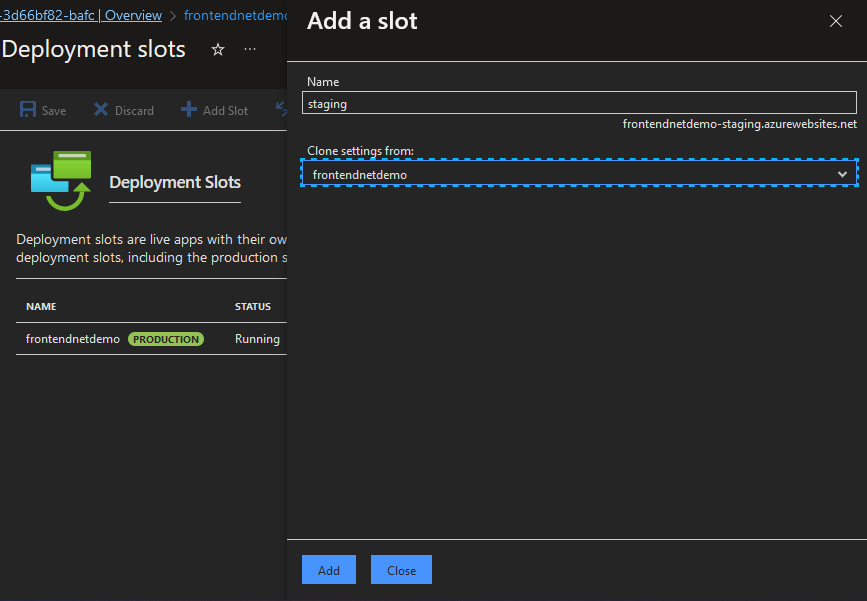 Fig. 9: Azure App Service’s deployment swap feature
Fig. 9: Azure App Service’s deployment swap feature
The key benefits of Azure App Service
Azure App service as a fully-managed service enables support for multiple languages and frameworks like ASP.NET, ASP.NET Core, Python, Node.js, PHP etc. It also supports high availability, scalability, integration with DevOps pipeline and deployment facility through containerized platform.
- Azure App Service is a managed HTTP-based platform for publishing web apps, REST APIs, and mobile and API apps as cross-platform environments.
- It can be containerized with Docker or Kubernetes clusters using Windows/Linux containers.
- The applications can be configured with a CI/CD pipeline using Azure DevOps, GitHub, or Bitbucket. The artifacts can be managed with Azure Container Registry promoting DevTest and staging to production environments.
- It provides over 50 SaaS application connectors for integration and global scaling with dedicated SLA benefits. The development environment can be integrated with Visual Studio or Visual Studio Code.
Deploying mobile apps through Azure App Service
Azure App Service allows provisioning cross-platform, native as well as responsive mobile applications using autoscaling and offline data synchronization features. It includes authentication support with Azure AD, SAP, Oracle, and SQL Server and offers push notifications as a feature.
Mobile apps can be deployed through Azure App service by setting the publish option to Code. The runtime stack can be set as Python or ASP.NET, based on the backend of the application. It can also be enabled to execute mobile apps on either Windows or Linux.
Once provisioned, the application settings can be updated, with “MobileAppsManagement_EXTENSION_VERSION” as the name and “latest” as the value.
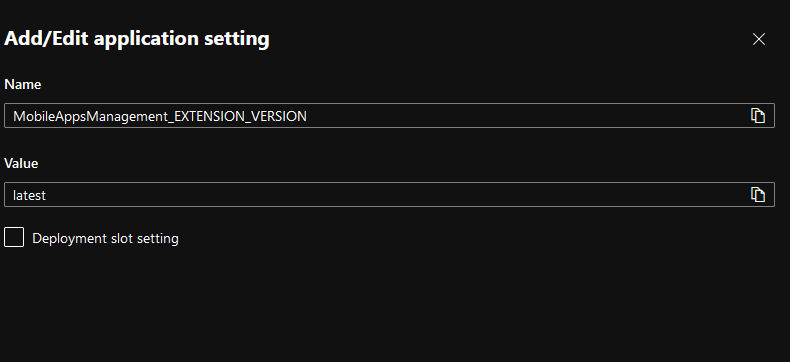 Fig. 10: Integrating app settings for mobile app configuration
Fig. 10: Integrating app settings for mobile app configuration
CI/CD for Azure frontends
The CI/CD pipeline can be configured for publishing Azure frontend applications. To set up the CI/CD pipeline for Azure App Service for frontends, go to Deployment Center and select the code repository from the dropdown menu.
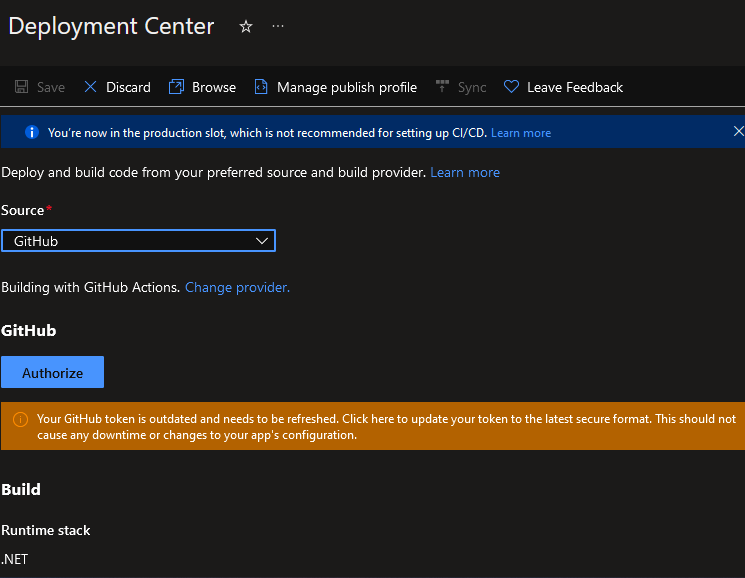 Fig. 11: CI/CD pipeline source control repository settings for Azure frontends
Fig. 11: CI/CD pipeline source control repository settings for Azure frontends
All files related to the build and release changes of the application are located in the /home/site/wwwroot directory. The build and release pipeline can be published directly from the packaged ZIP file and deployed to the staging slot with auto-swap turned on.
Monitoring the Azure DevOps release cycle of frontend applications
Monitoring is crucial when implementing a build and release pipeline, as it helps to pinpoint the root cause of application failures. It can also identify network issues like bandwidth bottlenecks. Monitoring can find delayed requests, along with requests that exceed the thresholds.
- If a user request gets significantly delayed, a notification mail will be sent.
- Requests that consume more Azure DevOps throughput units can be tracked by user agent and IP address details, along with the potential delay time.
- From the Azure DevOps pipeline, audit logs can be accessed and filtered to track issues like pipeline failure, build failure, and request too slow, as well as to display user activity logs and pipeline activity logs.
- Audit changes also include user permissions changes, deleted resources, branch policy modification, and access logs.
Docker Container deployment through Azure pipelines
Frontend applications (React or Vue.js with an ASP.NET web app, for instance) can be deployed through Azure App Service web apps using Docker containers, and the CI/CD pipeline can be configured using Docker.
- The pipeline variables can be declared by defining the trigger and the
BuildConfigurationsettings as Release andwebRepositoryas web. - The
docker@2task is required to build and deploy containers. It consists of the following settings as part of the task: commandspecifies the build and push features to execute in the pipeline.buildContextdefines the build path context.repositoryprovides the repository name.dockerfiledefines the relevant path of the Dockerfile.containerRegistryspecifies the container registry name.tagsprovides the tags applied on the container images.
For provisioning Azure App Service through a CI/CD deployment pipeline using a Docker container, the deploy stage of the container task should include the App Service instance name, subscription details, and the Docker container image name.
Deploying frontend web apps using AKS
Kubernetes is a platform for containerized application deployment where web applications can be built and deployed to clusters. A frontend application can be deployed as a service in the Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) cluster with a YAML manifest file. Here goes a sample yaml file used for deploying apps in AKS.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: aks-sample-linux-service
namespace: aks-sample-app
labels:
app: aks-sample-linux-app
spec:
selector:
app: aks-sample-linux-app
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
targetPort: 80
The frontend app can then be packaged as a container image and deployed to the Azure container registry as well before deployment to the AKS cluster.
Deploying microservices with frontends on Azure
Using event-driven architecture to design and build microservice-based applications provides the benefits of automated scaling, which include isolated points of failure, independent modules, and faster value delivery. Since microservice applications consist of individual services that communicate with each other with well-defined APIs, service integration and discovery can be managed through event triggering or a Pub/Sub model resource like Azure Event Grid.
- Frontend applications (web apps/API apps) can be deployed as separate modules that are to be built, deployed, and monitored independently. Microservices applications are built with loosely coupled architecture combined with independent modules.
- The microservice application consists of independent modules that provide autonomous scalability where each service can individually and automatically scale based on workload demand. It also lowers costs and reduces the potential downtime.
- The parallel deployment of applications by independent modules leads to isolated points of failure, where each service can be managed independently and have its own independent fault tolerance and fault handling capability.
- Since microservices are individual application modules that consist of well-defined interfaces, they can be built with a cross-platform environment and any programming language.
- Overall, microservice applications provide increased agility and value proportion.
The benefits of Azure Functions
Azure Functions is a managed event-based triggering platform that helps users build and deploy frontend applications as serverless microservices. It offers an easy-to-use, fast, and seamless integration platform for developers to execute serverless microservices with HTTP-based triggers.
It also offers a mobile app binding functionality for frontend deployment. For event-based triggering platforms or for real-time streaming, Azure Functions can integrate with Apache Kafka as an output extension to event-based triggering for invoking functions in response to Kafka topic messages. Moreover, it supports RabbitMQ, SignalR, and Azure Service Bus as an event-based trigger binding integration platform.
Workflow management through Azure Logic Apps
Azure Logic Apps is a managed workflow platform where automated workflows can be created with low or no code. It includes the benefits of a visual designer through which workflows integrating with applications, data, and services can be built.
- Azure Logic Apps can help deploy and run logic applications for frontend apps while offering private endpoints, Azure Virtual Network access, and deployment slots.
- It can smooth the process of building, debugging, and deploying apps on Windows, Linux, or OS X with cross-platform tools, and it offers simplified CI/CD pipeline management.
Deploying static web applications on Azure
Azure Static Web Apps is used to build and deploy applications from a source control repository for static content with the option of every code change to reflect directly on the frontend application.
With a static web application, the static contents are isolated from the web server; as a result, the contents can be streamed from the content delivery network (CDN).
Azure Static Web Apps offers multiple benefits:
- Provides a seamless web hosting environment for static content like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- Provides integrated API support with Azure Functions and allows adding code directly from a source control repository like GitHub or an Azure DevOps repository.
- Provides free SSL certificate renewal, as well as a seamless, built-in security model with authentication and authorization support with Azure AD.
- Azure Blob Storage to store static content and build modern web applications.
- Websites published through frameworks like VuePress can be integrated with Azure Functions, Azure API management, and Azure Container Apps.
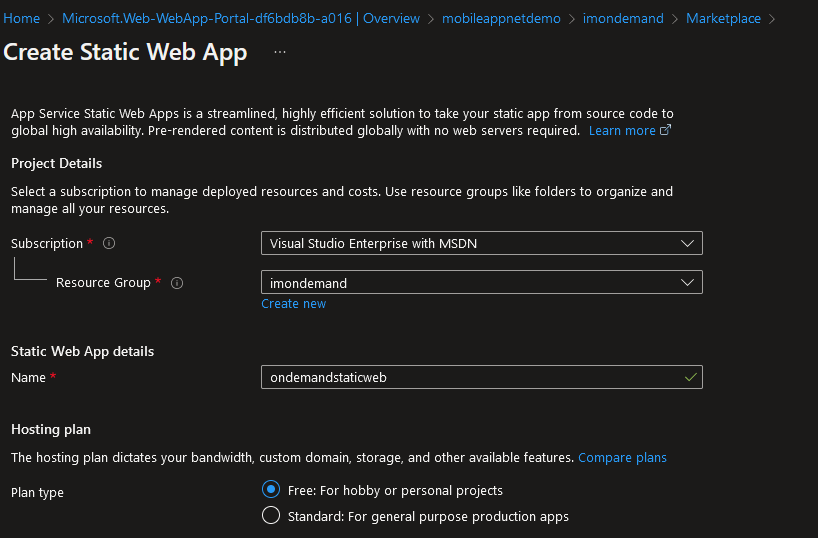 Fig 12: Deploying an Azure Static Web application
Fig 12: Deploying an Azure Static Web application
Integrating Azure Static Web Apps with Azure CDN
Azure CDN allows caching static content hosted in Azure Blob Storage. Azure CDN can be used to configure the custom domain endpoints (CNAME records) for a static web app, enabling users to deploy TLS/SSL certificates and specify the HTTP routing rules.
Configuring Azure CDN for hosting static web content
From Azure’s storage security and networking settings, new CDN endpoints can be provisioned, with the following pricing tiers:
- Microsoft CDN (classic)
- Standard Verizon
- Standard Akamai
- Premium Verizon
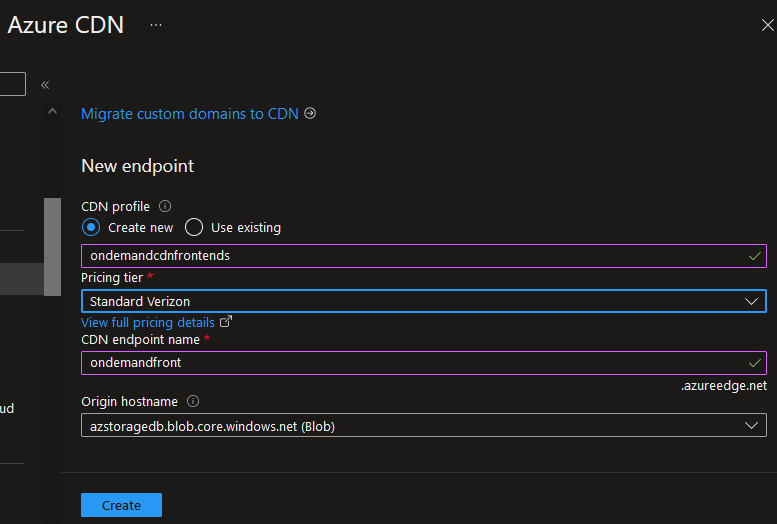 Fig. 13: Azure CDN configuration for storage account integration
Fig. 13: Azure CDN configuration for storage account integration
Once the CDN profile is configured, it can be integrated with Azure Static Web App with the Origin hostname field, Origin host headers, and host path settings. The static media objects can persist as the cache until the TTL expires.
Rehosting legacy frontend applications with Azure compute services
Another important option to consider when modernizing applications is rehosting legacy frontend web applications into Azure compute services, such as Azure Virtual Machines (Azure VMs) or Azure Container Instances. The legacy applications can be deployed to Azure by using a rehost or lift-and-shift approach with tools like Azure Migrate.
- Deployments of legacy web applications (such as JSP/ASP.NET webforms, MVC 3, MVC 4) can be published on IIS web servers or Tomcat /JBoss web servers on Azure VMs.
- Azure Migrate is a managed service that provides end-to-end guidance and insights for migrating web apps to Azure VMs by discovery, assessment, and migration of on-premises VMs to Azure.
- Azure compute services provide intelligent insight for VMs that help specify the appropriate VM infrastructure capacity and compute units.
- Azure compute services assign compatibility reporting tools to potential remediating features.
Caching the contents of frontend apps deployed on VMs
Caching web apps or frontend applications can be managed through Azure Cache for Redis. It allows for storing caching content as key/value pairs based on object-based storage keys and the caching content/MIME type are being determined.
Deploying Azure web apps through Azure Container Instances (ACI)
Azure web apps can be containerized on both Windows and Linux to create an easy-to-use, seamless managed platform for development and deployment. Apps can be deployed with a single artifact and its dependencies targeting a specific platform. The streamlined CI/CD workflow can be managed through Docker Hub, Azure Container Registry (ACR), or GitHub.
- The container instances are responsible for published app images to Docker Hub or ACR.
- Azure App Service can pull images with credentials or with Azure AD Managed Identity Platform authenticated through a service principal.
- The service connector manages other resources, and while new images are available to the ACR, it triggers an automated deployment to the app service platform.
Summary
Azure frontends (such as web apps, mobile or API apps) are managed platform as service (PaaS) services that can be deployed in cross-platform environments. In this article, we covered the various deployment options of application frontends on Azure.
The Azure App Service platform provides automated scaling, high availability, reliability, and guaranteed SLA. Frontend apps deployed through Azure App Service offer the benefits of authentication and authorization through Azure AD pass-through authentication.
Security is managed through Microsoft Defender for Cloud. Azure Security Center provides security incident reports, with recommendations such as enablement of web applications through HTTPS protocol or encryption of data at rest and in transit.
TLS/SSL settings should be enforced with integrated certificates. It’s recommended to use managed identity for authorization to obtain Azure AD tokens for secure access by users to apps.
The basic Azure App Service plan offers backup and restore capabilities for Azure web apps. It also allows the secure connectivity of frontend apps through Azure private endpoints. It enables access through private IP addresses deployed over Azure Virtual Network.